Effects
Effects are used in OpenShot to enhance or modify the audio or video of a clip. They can modify pixels and audio data, and can generally enhance your video projects. Each effect has its own set of properties, most of which can be animated over time, for example varying the Brightness & Contrast of a clip over time.
Effects can be added to any clip by dragging and dropping them from the Effects tab onto a clip. Each effect is represented by a small colored icon and the first letter of the effect name. Note: Pay close attention to where the play-head (i.e. red playback line) is. Key frames are automatically created at the current playback position, to help create animations quickly.
To view an effect’s properties, right-click on the effect icon, revealing the context menu, and choose Properties.
The property editor will appear, where you can edit these properties. Properties appear alphabetically in the dock,
with filter options available at the top. Hold Ctrl and click multiple
effect icons to select them all, the Properties dock will show an entry such as
3 Selections so you can adjust their common settings in one step. See Clip Properties.
To adjust a property:
Drag the slider for coarse changes.
Double-click to enter precise values.
Right/double-click for non-numerical options.
Effect properties are integral to the Animation system. When you modify an effect property, a keyframe is generated at the current playhead position. For a property to span the entire clip, position the playhead at or before the clip’s start before making adjustments. A convenient way to identify a clip’s start is by utilizing the ‘next/previous marker’ feature on the Timeline toolbar.
List of Effects
OpenShot Video Editor has a total of 27 built-in video and audio effects: 18 video effects and 9 audio effects. These effects can be added to a clip by dragging the effect onto a clip. The following table contains the name and short description of each effect.
Icon |
Effect Name |
Effect Description |
|---|---|---|
Analog Tape |
Vintage home-video wobble, bleed, and snow. |
|
Alpha Mask / Wipe Transition |
Grayscale mask transition between images. |
|
Bars |
Add colored bars around your video. |
|
Blur |
Adjust image blur. |
|
Brightness & Contrast |
Modify frame’s brightness and contrast. |
|
Caption |
Add text captions to any clip. |
|
Chroma Key (Greenscreen) |
Replace color with transparency. |
|
Color Map / Lookup |
Adjust colors using 3D LUT lookup tables (.cube format). |
|
Color Saturation |
Adjust color intensity. |
|
Color Shift |
Shift image colors in various directions. |
|
Crop |
Crop out parts of your video. |
|
Deinterlace |
Remove interlacing from video. |
|
Hue |
Adjust hue / color. |
|
Lens Flare |
Simulate sunlight hitting a lens with flares. |
|
Negative |
Produce a negative image. |
|
Object Detector |
Detect objects in video. |
|
Outline |
Add outline around any image or text. |
|
Pixelate |
Increase or decrease visible pixels. |
|
Sharpen |
Boost edge contrast to make video details look crisper. |
|
Shift |
Shift image in different directions. |
|
Spherical Projection |
Flatten or project 360° and fisheye footage. |
|
Stabilizer |
Reduce video shake. |
|
Tracker |
Track bounding box in video. |
|
Wave |
Distort image into a wave pattern. |
|
Compressor |
Reduce loudness or amplify quiet sounds. |
|
Delay |
Adjust audio-video synchronism. |
|
Distortion |
Clip audio signal for distortion. |
|
Echo |
Add delayed sound reflection. |
|
Expander |
Make loud parts relatively louder. |
|
Noise |
Add random equal-intensity signals. |
|
Parametric EQ |
Adjust frequency volume in audio. |
|
Robotization |
Transform audio into robotic voice. |
|
Whisperization |
Transform audio into whispers. |
Effect Properties
Below is a list of common effect properties, shared by all effects in OpenShot. To view an effect’s properties, right click and choose Properties. The property editor will appear, where you can change these properties. Note: Pay close attention to where the play-head (i.e. red playback line) is. Key frames are automatically created at the current playback position, to help quickly create animations.
See the table below for a list of common effect properties. Only the common properties that all effects share are listed here. Each effect also has many unique properties, which are specific to each effect, see Video Effects for more information on individual effects and their unique properties.
Effect Property Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|
Duration |
Float |
The length of the effect (in seconds). Read-only property. Most effects default to the length of a clip. This property is hidden when an effect belongs to a clip. |
End |
Float |
The end trimming position of the effect (in seconds). This property is hidden when an effect belongs to a clip. |
ID |
String |
A randomly generated GUID (globally unique identifier) assigned to each effect. Read-only property. |
Parent |
String |
The parent object to this effect, which makes many of these keyframe values initialize to the parent value. |
Position |
Float |
The position of the effect on the timeline (in seconds). This property is hidden when an effect belongs to a clip. |
Start |
Float |
The start trimming position of the effect (in seconds). This property is hidden when an effect belongs to a clip. |
Track |
Int |
The layer which holds the effect (higher tracks are rendered on top of lower tracks). This property is hidden when an effect belongs to a clip. |
Apply Before Clip |
Boolean |
Apply this effect before the Clip processes keyframes? (default is Yes) |
Duration
The Duration property is a float value indicating the length of the effect in seconds. This is a Read-only property. This is calculated by: End - Start. To modify duration, you must edit the Start and/or End effect properties.
NOTE: Most effects in OpenShot default the effect duration to the clip duration, and hide this property from the editor.
End
The End property defines the trimming point at the end of the effect in seconds, allowing you to control how much of the effect is visible in the timeline. Changing this property will impact the Duration effect property.
NOTE: Most effects in OpenShot default this property to match the clip, and hide this property from the editor.
ID
The ID property holds a randomly generated GUID (Globally Unique Identifier) assigned to each effect, ensuring its uniqueness. This is a Read-only property, and assigned by OpenShot when an effect is created.
Track
The Track property is an integer indicating the layer on which the effect is placed. Effects on higher tracks are rendered above those on lower tracks.
NOTE: Most effects in OpenShot default this property to match the clip, and hide this property from the editor.
Effect Parent
The Parent property of an effect sets the initial keyframe values to a parent effect. For example, if many effects all point to the
same parent effect, they will inherit all their initial properties, such as font size, font color, and background color for a Caption effect.
In the example of many Caption effects using the same Parent effect, it is an efficient way to manage a large number of these effects.
NOTE: The parent property for effects should be linked to the same type of parent effect, otherwise their default initial values
will not match. Also see Clip Parent.
Position
The Position property determines the effect’s position on the timeline in seconds, with 0.0 indicating the beginning.
NOTE: Most effects in OpenShot default this property to match the clip, and hide this property from the editor.
Start
The Start property defines the trimming point at the beginning of the effect in seconds. Changing this property will impact the Duration effect property.
NOTE: Most effects in OpenShot default this property to match the clip, and hide this property from the editor.
Sequencing
Effects are normally applied before the Clip processes keyframes. This allows the effect to process the raw image of
the clip, before the clip applies properties such as scaling, rotation, location, etc… Normally, this is the preferred
sequence of events, and this is the default behavior of effects in OpenShot. However, you can optionally override this
behavior with the Apply Before Clip Keyframes property.
If you set the Apply Before Clip Keyframes property to No, the effect will be sequenced after the clip scales, rotates,
and applies keyframes to the image. This can be useful on certain effects, such as the Mask effect, when you want
to animate a clip first and then apply a static mask to the clip.
Video Effects
Effects are generally divided into two categories: video and audio effects. Video effects modify the image and pixel data of a clip. Below is a list of video effects, and their properties. Often it is best to experiment with an effect, entering different values into the properties, and observing the results.
Analog Tape
The Analog Tape effect emulates consumer tape playback: horizontal line wobble (“tracking”), chroma bleed, luma softness, grainy snow, a bottom tracking stripe, and short static bursts. All controls are key-framable and the noise is deterministic (seeded from the effect’s ID with an optional offset), so renders are repeatable.
Property Name |
Description |
|---|---|
tracking |
|
bleed |
|
softness |
|
noise |
|
stripe |
|
static_bands |
|
seed_offset |
|
Usage notes
Subtle “home video”:
tracking=0.25,bleed=0.20,softness=0.20,noise=0.25,stripe=0.10,static_bands=0.05.Bad tracking / head clog:
tracking=0.8–1.0,stripe=0.6–0.9,noise=0.6–0.8,static_bands=0.4–0.6,softness<=0.2, and setbleedto about 0.3.Color fringing only: raise
bleed(about 0.5) and keep other controls low.Different but repeatable snow: leave the effect ID alone (for deterministic output) and change
seed_offsetto get a new, still-repeatable pattern.
Alpha Mask / Wipe Transition
The Alpha Mask / Wipe Transition effect leverages a grayscale mask to create a dynamic transition between two images or video clips. In this effect, the light areas of the mask reveal the new image, while the dark areas conceal it, allowing for creative and custom transitions that go beyond standard fade or wipe techniques. This effect only affects the image, and not the audio track.
Property Name |
Description |
|---|---|
brightness |
|
contrast |
|
reader |
|
replace_image |
|
Bars
The Bars effect adds colored bars around your video frame, which can be used for aesthetic purposes, to frame the video within a certain aspect ratio, or to simulate the appearance of viewing content on a different display device. This effect is particularly useful for creating a cinematic or broadcast look.
Property Name |
Description |
|---|---|
bottom |
|
color |
|
left |
|
right |
|
top |
|
Blur
The Blur effect softens the image, reducing detail and texture. This can be used to create a sense of depth, draw attention to specific parts of the frame, or simply to apply a stylistic choice for aesthetic purposes. The intensity of the blur can be adjusted to achieve the desired level of softness.
Property Name |
Description |
|---|---|
horizontal_radius |
|
iterations |
|
sigma |
|
vertical_radius |
|
Brightness & Contrast
The Brightness & Contrast effect allows for the adjustment of the overall lightness or darkness of the image (brightness) and the difference between the darkest and lightest parts of the image (contrast). This effect can be used to correct poorly lit videos or to create dramatic lighting effects for artistic purposes.
Property Name |
Description |
|---|---|
brightness |
|
contrast |
|
Caption
Add text captions on top of your video. We support both VTT (WebVTT) and SubRip (SRT) subtitle file formats. These formats are used to display captions or subtitles in videos. They allow you to add text-based subtitles to video content, making it more accessible to a wider audience, especially for those who are deaf or hard of hearing. The Caption effect can even animate the text fading in/out, and supports any font, size, color, and margin. OpenShot also has an easy-to-use Caption editor, where you can quickly insert captions at the playhead position, or edit all your caption text in one place.
:caption: Show a caption, starting at 5 seconds and ending at 10 seconds.
00:00:05.000 --> 00:00:10.000
Hello, welcome to our video!
Property Name |
Description |
|---|---|
background |
|
background_alpha |
|
background_corner |
|
background_padding |
|
caption_font |
|
caption_text |
|
color |
|
fade_in |
|
fade_out |
|
font_alpha |
|
font_size |
|
left |
|
line_spacing |
|
right |
|
stroke |
|
stroke_width |
|
top |
|
Chroma Key (Greenscreen)
The Chroma Key (Greenscreen) effect replaces a specific color (or chroma) in the video (commonly green or blue) with transparency, allowing for the compositing of the video over a different background. This effect is widely used in film and television production for creating visual effects and placing subjects in settings that would be otherwise impossible or impractical to shoot in.
Property Name |
Description |
|---|---|
color |
|
threshold |
|
halo |
|
keymethod |
|
Color Map / Lookup
The Color Map effect applies a 3D LUT (Lookup Table) to your footage, instantly transforming its colors to achieve a consistent look or mood. A 3D LUT is simply a table that remaps every input hue to a new output palette. With separate keyframe curves for red, green, and blue channels, you can precisely control, and even animate, how much each channel is influenced by the LUT, making it easy to fine-tune or blend your grade over time.
LUT files (.cube format) can be downloaded from many online resources, including free packs on photography blogs or marketplaces, such as https://freshluts.com/. OpenShot includes a selection of popular LUTs designed for Rec 709 gamma out of the box.
Property Name |
Description |
|---|---|
lut_path |
|
intensity |
|
intensity_r |
|
intensity_g |
|
intensity_b |
|
Gamma and Rec 709
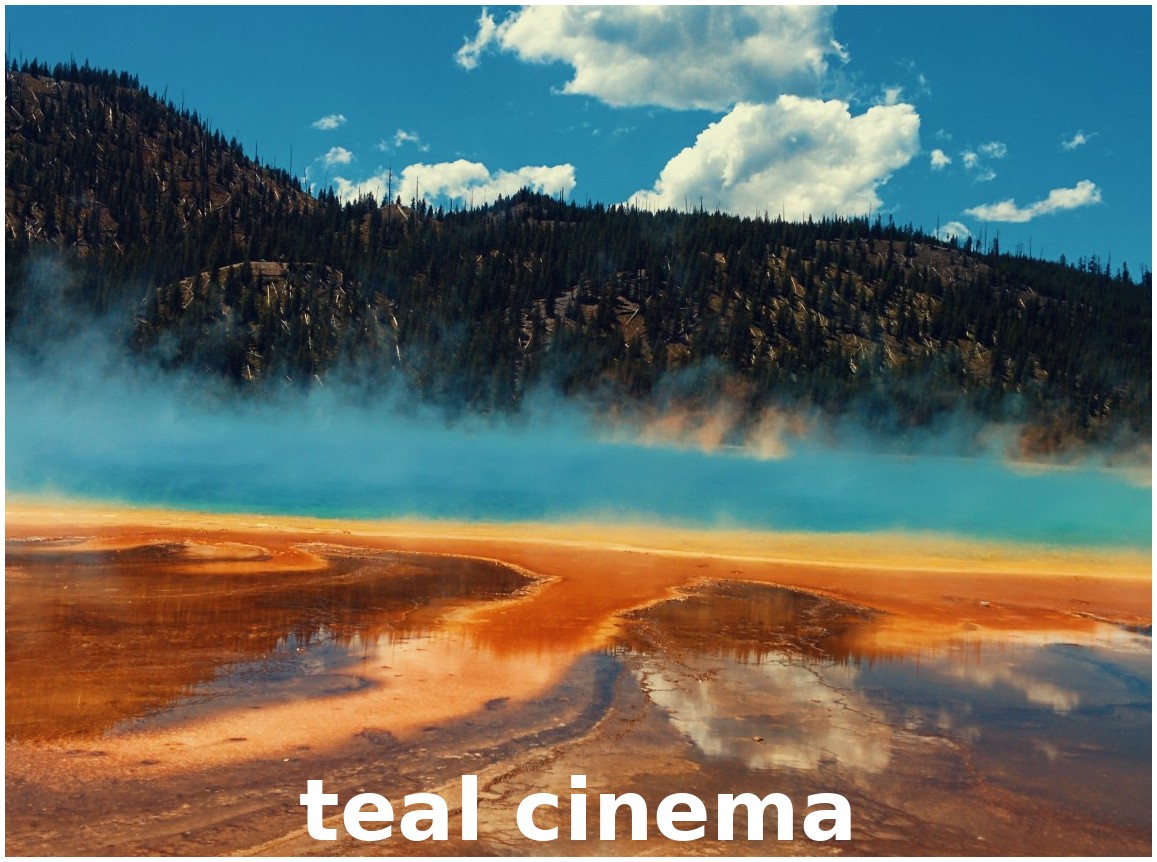
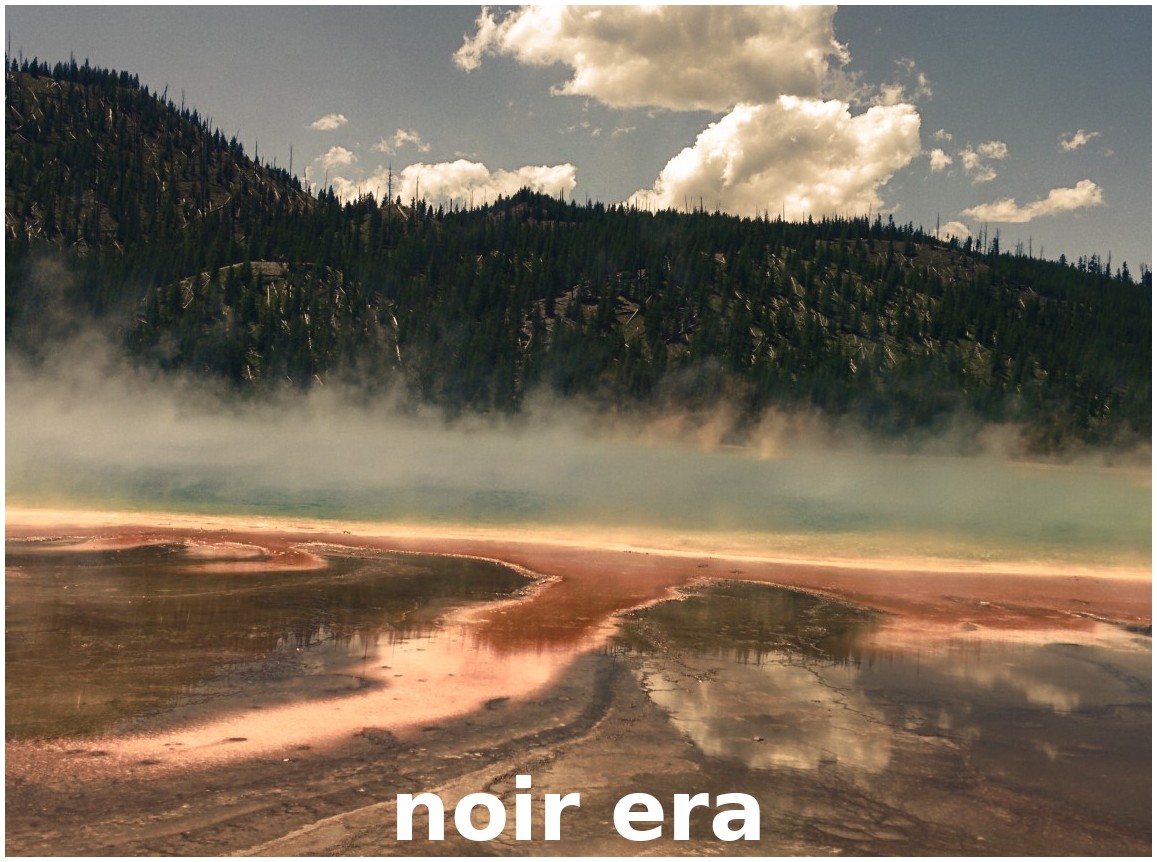
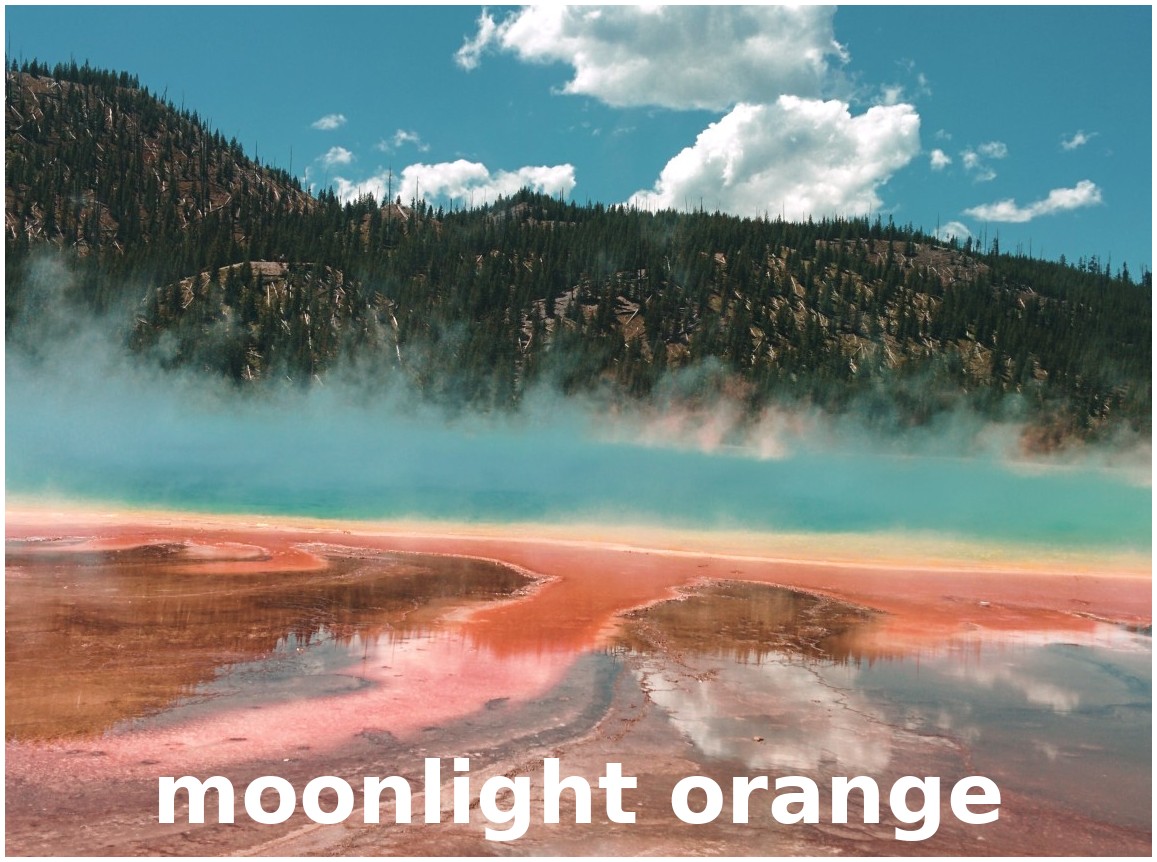
Gamma is the way video systems brighten or darken the midtones of an image. Rec 709 is the standard gamma curve used for most HD and online video today. By shipping with Rec 709 LUTs, OpenShot makes it simple to apply a grade that matches the vast majority of footage you’ll edit.
If your camera or workflow uses a different gamma (for example a LOG profile), you can still use a LUT made for that curve. Simply use a .cube file designed for your gamma under the Color Map effect’s LUT Path. Just be sure your footage gamma matches the LUT gamma—or the colors may look incorrect.
The following Rec 709 LUT files are included in OpenShot, organized into the following categories:
Cinematic & Blockbuster
Dark & Moody
Film Stock & Vintage
Teal & Orange Vibes
Utility & Correction
Vibrant & Colorful
Color Saturation
The Color Saturation effect adjusts the intensity and vibrancy of colors within the video. Increasing saturation can make colors more vivid and eye-catching, while decreasing it can create a more subdued, almost black-and-white appearance.
Property Name |
Description |
|---|---|
saturation |
|
saturation_B |
|
saturation_G |
|
saturation_R |
|
Color Shift
Shift the colors of an image up, down, left, and right (with infinite wrapping).
Each pixel has 4 color channels:
Red, Green, Blue, and Alpha (i.e. transparency)
Each channel value is between 0 and 255
The Color Shift effect simply “moves” or “translates” a specific color channel on the X or Y axis. Not all video and image formats support an alpha channel, and in those cases, you will not see any changes when adjusting the color shift of the alpha channel.
Property Name |
Description |
|---|---|
alpha_x |
|
alpha_y |
|
blue_x |
|
blue_y |
|
green_x |
|
green_y |
|
red_x |
|
red_y |
|
Crop
The Crop effect removes unwanted outer areas from the video frame, allowing you to focus on a particular part of the
shot, change the aspect ratio, or remove distracting elements from the edges of the frame. This effect is the
primary method for cropping a Clip in OpenShot. The left, right, top, and bottom key-frames can
even be animated, for a moving and resizing cropped area. You can leave the cropped area blank, or you can
dynamically resize the cropped area to fill the screen.
You can quickly add this effect by right-clicking a clip and choosing Crop. When active, blue crop handles appear in the video preview so you can adjust the crop visually.
Property Name |
Description |
|---|---|
bottom |
|
left |
|
right |
|
top |
|
x |
|
y |
|
resize |
|
Deinterlace
The Deinterlace effect is used to remove interlacing artifacts from video footage, which are commonly seen as horizontal lines across moving objects. This effect is essential for converting interlaced video (such as from older video cameras or broadcast sources) into a progressive format suitable for modern displays.
Property Name |
Description |
|---|---|
isOdd |
|
Hue
The Hue effect adjusts the overall color balance of the video, changing the hues without affecting the brightness or saturation. This can be used for color correction or to apply dramatic color effects that transform the mood of the footage.
Property Name |
Description |
|---|---|
hue |
|
Lens Flare
The Lens Flare effect simulates bright light hitting your camera lens, creating glowing halos, colored rings and gentle glares over your footage. Reflections are automatically placed along a line from the light source toward the center of the frame. You can animate any property with keyframes to follow your action or match your scene.
Property Name |
Description |
|---|---|
x |
|
y |
|
brightness |
|
size |
|
spread |
|
tint_color |
|
Negative
The Negative effect inverts the colors of the video, producing an image that resembles a photographic negative. This can be used for artistic effects, to create a surreal or otherworldly look, or to highlight specific elements within the frame.
Object Detector
The Object Detector effect employs machine learning algorithms (such as neural networks) to identify and highlight objects within the video frame. It can recognize multiple object types, such as vehicles, people, animals, and more! This can be used for analytical purposes, to add interactive elements to videos, or to track the movement of specific objects across the frame.
Class Filters & Confidence
To adjust the detection process to your specific needs, the Object Detector includes properties for class filters
and confidence thresholds. By setting a class filter, such as “Truck” or “Person,” you can instruct the detector to
focus on specific types of objects, limiting the types of objects tracked. The confidence threshold allows you to
set a minimum level of certainty for detections, ensuring that only objects detected with a confidence level above
this threshold are considered, which helps in reducing false positives and focusing on more accurate detections.
How Parenting Works
Once you have tracked objects, you can “parent” other Clips to them. This means that the second clip, which could be a graphic, text, or another video layer, will now follow the tracked object as if it’s attached to it. If the tracked object moves to the left, the child clip moves to the left. If the tracked object grows in size (gets closer to the camera), the child clip also scales up. For parented clips to appear correctly, they must be on a Track higher than the tracked objects, and set the appropriate Scale property.
See Clip Parent.
Properties
Property Name |
Description |
|---|---|
class_filter |
|
confidence_threshold |
|
display_box_text |
|
display_boxes |
|
selected_object_index |
|
draw_box |
|
box_id |
|
x1 |
|
y1 |
|
x2 |
|
y2 |
|
delta_x |
|
delta_y |
|
scale_x |
|
scale_y |
|
rotation |
|
visible |
|
stroke |
|
stroke_width |
|
stroke_alpha |
|
background_alpha |
|
background_corner |
|
background |
|
Outline
The Outline effect adds a customizable border around images or text within a video frame. It works by extracting the image’s alpha channel, blurring it to generate a smooth outline mask, and then combining this mask with a solid color layer. Users can adjust the outline’s width as well as its color components (red, green, blue) and transparency (alpha), allowing for a wide range of visual styles. This effect is ideal for emphasizing text, creating visual separation, and adding an artistic flair to your videos.
Property Name |
Description |
|---|---|
width |
|
red |
|
green |
|
blue |
|
alpha |
|
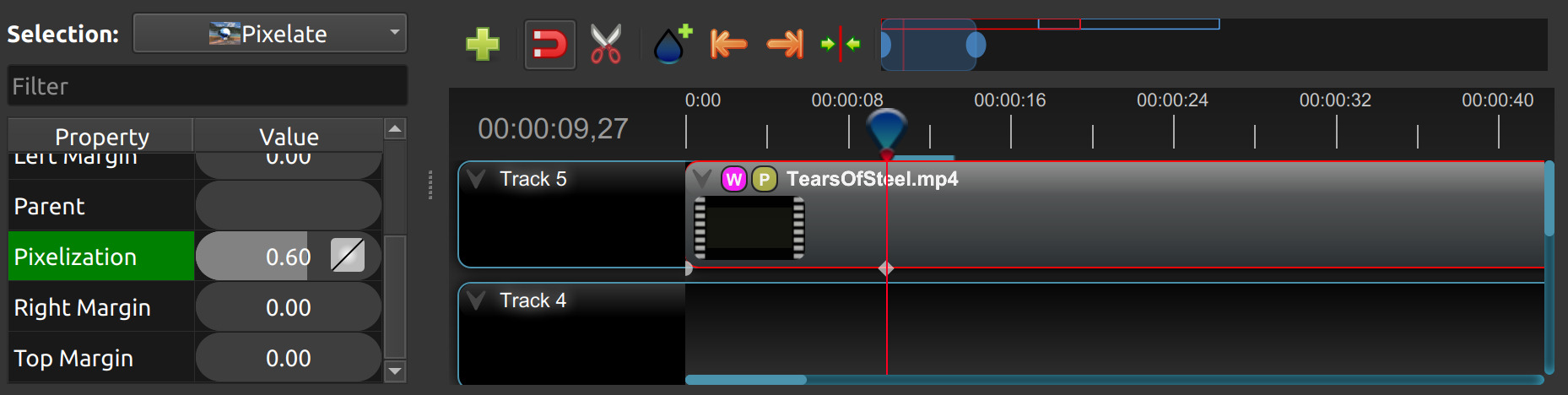
Pixelate
The Pixelate effect increases or decreases the size of the pixels in the video, creating a mosaic-like appearance. This can be used to obscure details (such as faces or license plates for privacy reasons), or as a stylistic effect to evoke a retro, digital, or abstract aesthetic.
Property Name |
Description |
|---|---|
bottom |
|
left |
|
pixelization |
|
right |
|
top |
|
Shift
The Shift effect moves the entire image in different directions (up, down, left, and right with infinite wrapping), creating a sense of motion or disorientation. This can be used for transitions, to simulate camera movement, or to add dynamic motion to static shots.
Property Name |
Description |
|---|---|
x |
|
y |
|
Spherical Projection
The Spherical Projection effect flattens 360° or fisheye footage into a normal rectangular view, or generates fisheye output. Steer a virtual camera with yaw, pitch, and roll. Control the output view with FOV. Choose the input type (equirect or one of the fisheye models), pick a projection mode for the output, and select a sampling mode that balances quality and speed. This is ideal for keyframed “virtual camera” moves inside 360° clips and for converting circular fisheye shots.
Property Name |
Description |
|---|---|
yaw |
|
pitch |
|
roll |
|
fov |
|
in_fov |
|
projection_mode |
|
input_model |
|
invert |
|
interpolation |
|
Usage notes
Flatten a fisheye clip to a normal view: Set Input Model to the correct fisheye type, set In FOV to your lens coverage (often 180), choose Projection Mode = Sphere or Hemisphere, then frame with Yaw/Pitch/Roll and Out FOV.
Reframe an equirect clip: Set Input Model = Equirectangular, pick Sphere (full) or Hemisphere (front/back). Invert on equirect is equivalent to yaw +180 and does not mirror.
Create a fisheye output: Choose one of the Fisheye projection modes (2..5). Out FOV controls disk coverage (180 gives a classic circular fisheye).
If the image looks mirrored, turn Invert off. If you need the back view on equirect, use Invert or add +180 to Yaw.
If the output looks soft or aliased, reduce Out FOV or increase export resolution. Auto interpolation adapts the filter to scaling.
Stabilizer
The Stabilizer effect reduces unwanted shake and jitter in handheld or unstable video footage, resulting in smoother, more professional-looking shots. This is particularly useful for action scenes, handheld shots, or any footage where a tripod was not used.
Property Name |
Description |
|---|---|
zoom |
|
Tracker
The Tracker effect allows for the tracking of a specific object or area within the video frame across multiple frames.
This can be used for motion tracking, adding effects or annotations that follow the movement of objects, or for
stabilizing footage based on a tracked point.When tracking an object, be sure to select the entire object, which is
visible at the start of a clip, and choose one of the following Tracking Type algorithms. The tracking algorithm
then follows this object from frame to frame, recording its position, scale, and sometimes rotation.
Tracking Type
KCF: (default) A blend of Boosting and MIL strategies, employing correlation filters on overlapping areas from ‘bags’ to accurately track and predict object movement. It offers higher speed and accuracy and can stop tracking when the object is lost but struggles to resume tracking after losing the object.
MIL: Improves upon Boosting by considering multiple potential positives (‘bags’) around the definite positive object, increasing robustness to noise and maintaining good accuracy. However, it shares the Boosting Tracker’s drawbacks of low speed and difficulty in stopping tracking when the object is lost.
BOOSTING: Utilizes the online AdaBoost algorithm to enhance the classification of tracked objects by focusing on incorrectly classified ones. It requires setting the initial frame and treats nearby objects as background, adjusting to new frames based on maximum score areas. It’s known for accurate tracking but suffers from low speed, noise sensitivity, and difficulty stopping tracking upon object loss.
TLD: Decomposes tracking into tracking, learning, and detection phases, allowing for adaptation and correction over time. While it can handle object scaling and occlusions reasonably well, it may behave unpredictably, with instability in tracking and detection.
MEDIANFLOW: Based on the Lucas-Kanade method, it analyzes forward and backward movement to estimate trajectory errors for real-time position prediction. It’s fast and accurate under certain conditions but can lose track of fast-moving objects.
MOSSE: Utilizes adaptive correlations in Fourier space to maintain robustness against lighting, scale, and pose changes. It boasts very high tracking speeds and is better at continuing tracking after loss, but it may persist in tracking an absent object.
CSRT: Employs spatial reliability maps to adjust filter support, enhancing the ability to track non-rectangular objects and perform well even with object overlaps. However, it is slower and may not operate reliably when the object is lost.
How Parenting Works
Once you have a tracked object, you can “parent” other Clips to it. This means that the second clip, which could be a graphic, text, or another video layer, will now follow the tracked object as if it’s attached to it. If the tracked object moves to the left, the child clip moves to the left. If the tracked object grows in size (gets closer to the camera), the child clip also scales up. For parented clips to appear correctly, they must be on a Track higher than the tracked objects, and set the appropriate Scale property.
See Clip Parent.
Properties
Property Name |
Description |
|---|---|
draw_box |
|
box_id |
|
x1 |
|
y1 |
|
x2 |
|
y2 |
|
delta_x |
|
delta_y |
|
scale_x |
|
scale_y |
|
rotation |
|
visible |
|
stroke |
|
stroke_width |
|
stroke_alpha |
|
background_alpha |
|
background_corner |
|
background |
|
Wave
The Wave effect distorts the image into a wave-like pattern, simulating effects like heat haze, water reflections, or other forms of distortion. The speed, amplitude, and direction of the waves can be adjusted.
Property Name |
Description |
|---|---|
amplitude |
|
multiplier |
|
shift_x |
|
speed_y |
|
wavelength |
|
Audio Effects
Audio effects modify the waveforms and audio sample data of a clip. Below is a list of audio effects, and their properties. Often it is best to experiment with an effect, entering different values into the properties, and observing the results.
Compressor
The Compressor effect in audio processing reduces the dynamic range of the audio signal, making loud sounds quieter and quiet sounds louder. This creates a more consistent volume level, useful for balancing the loudness of different audio sources or for achieving a particular sound characteristic in music production.
Property Name |
Description |
|---|---|
attack |
|
bypass |
|
makeup_gain |
|
ratio |
|
release |
|
threshold |
|
Delay
The Delay effect adds an echo to the audio signal, repeating the sound after a short delay. This can create a sense of space and depth in the audio, and is commonly used for creative effects in music, sound design, and audio post-production.
Property Name |
Description |
|---|---|
delay_time |
|
Distortion
The Distortion effect intentionally clips the audio signal, adding harmonic and non-harmonic overtones. This can create a gritty, aggressive sound characteristic of many electric guitar tones and is used for both musical and sound design purposes.
Property Name |
Description |
|---|---|
distortion_type |
|
input_gain |
|
output_gain |
|
tone |
|
Echo
The Echo effect, similar to delay, repeats the audio signal at intervals, but with a focus on creating a distinct repetition of sound that mimics natural echoes. This can be used to simulate acoustic environments or for creative sound effects.
Property Name |
Description |
|---|---|
echo_time |
|
feedback |
|
mix |
|
Expander
The Expander effect increases the dynamic range of audio, making quiet sounds quieter and leaving loud sounds unaffected. This is the opposite of compression and is used to reduce background noise or increase the dynamic impact of audio.
Property Name |
Description |
|---|---|
attack |
|
bypass |
|
makeup_gain |
|
ratio |
|
release |
|
threshold |
|
Noise
The Noise effect adds random, equal-intensity signals across the frequency spectrum to the audio, simulating the sound of white noise. This can be used for sound masking, as a component in sound design, or for testing and calibration purposes.
Property Name |
Description |
|---|---|
level |
|
Parametric EQ
The Parametric EQ (Equalizer) effect allows for precise adjustments to the volume level of specific frequency ranges in the audio signal. This can be used for corrective measures, such as removing unwanted tones, or creatively, to shape the tonal balance of the audio.
Property Name |
Description |
|---|---|
filter_type |
|
frequency |
|
gain |
|
q_factor |
|
Robotization
The Robotization effect transforms the audio to sound mechanical or robotic, by applying a combination of pitch modulation and synthesis techniques. This effect is widely used for character voices in media, creative music production, and sound design.
Property Name |
Description |
|---|---|
fft_size |
|
hop_size |
|
window_type |
|
Whisperization
The Whisperization effect transforms the audio to mimic a whispering voice, often by filtering out certain frequencies and adding noise. This can be used for artistic effects in music, sound design for film and video, or in audio storytelling to convey secrecy or intimacy.
Property Name |
Description |
|---|---|
fft_size |
|
hop_size |
|
window_type |
|
For more info on key frames and animation, see Animation.
















































































